Table of Contents
- Package managers
- System info
- Command & Bash snippets
- System Tools and 3rd party utilities command snippets
- Tips & tricks
- ProtonVPN connections
- Systemd
- Xrandr
- nmcli & Networking
- Packet Capturing
- SELinux
- DNF
- Adguard Home
- NFS
- NTP
- Podman
- Package management with DNF
- Logical Volume Managment
- CIFS
- GRUB
- User management
- Docker
- Oracle SBC
- TrueNAS
- Unzip
- Display Management
- Xorg
- Rclone
- Du
- Note
- Markdown
- Youtube downloading
- Serial Communication
- Jekyll
- ChatGPT CLI
- Rust
- Zsh
- Curl
- Snapper
- Bspwm
- Tmux
- Ranger
- Diff
- Unsorted helpful one liners
Package managers
Apt
- Query PPA for packages
apt-cache search <package-name> - Query PPA for NVIDIA package
apt-cache search nvidia
RHEL
- Reinstall all packages on system
dnf reinstall $(rpm -qa) - Change default python3 version
RHEL uses alternatives to manage different python3 versions , change the default using the commands below
```bash
sudo alternatives --install /usr/bin/python3 python3 /usr/bin/pythonx.x 1
sudo alternatives --install /usr/bin/python3 python3 /usr/bin/pythonx.xx 2
```
- Check config
sudo alternatives --config python3 - Ensure pip is updated to pythonx.xx
pythonX -m ensurepip --upgrade pythonX -m pip install --upgrade pip
System info
Create drive for mounting usb using fdisk
- For UEFI systems
- Partition Table : GPT
- Partition Type : EFI System Partition
- Filesystem: FAT32
- For BIOS systems
- Partition Table : MBR
- Partition Type : Primary
- Filesystem: FAT32 or ext4 (FAT32 preferred )
- For everything else
- Partition Table : MBR
- Partition Type : Primary
- Filesystem: FAT32
Downgrading kernel
-
Install Image, Headers , and generic Headers for the kernel version you are choosing
-
Install all 3 files , last time I was downgrading an ubuntu 24.04 distro using Kernel Version : 6.8.0-48-generic down to 5.8.5
-
Update grub config
System Memory
- Using /proc/meminfo
cat /proc/meminfo - Using free
free -h - Using vmstat
vmstat -s - Using dmidecode
sudo dmidecode -t memory - Using inxi
lsb_release
cat /etc/os-release
Swap files
When setting up swap files , the size of the partition used for a swap file depends on the size of the host systems memory.
-
If your system has 2 GB or less , the swap file should be 2-4 times the amount of ram
-
If your system has 4-8 GB of ram , the swap file size only needs to be 1-2 times the amount of RAM
-
If your system has 8-16 GB of ram , the swap file size should be 0.5-1 times the amount of ram
UEFI & Legacy BIOS mode
- Check if you’re booted into UEFI using /sys/firmware
ls /sys/firmware/efi - Check if you’re booted into UEFI using efibootmgr ( only works in UEFI mode )
sudo efibootmgr
Note: If you see any contents in the /sys/firmware/efi directory , then you will know you are currently using UEFI mode
Command & Bash snippets
- Turn off TCP Segmentation Offload and Generic Receive Offload
sudo ethtool -K <interface> tso off gro off - Write iso image to usb
sudo dd if=/path/to/distro.iso of=/dev/sdX bs=4M status=progress oflag=sync - Bash difference between $() and ${}
”${}” : Used for referencing variables in a script
- Example
```bash
echo ${var} something
```
”$()” : Used for running commands in a subshell
- Example
```bash
echo "Path $(basename /home/user/Downloads)
```
-
Redirect both STDOUT and STDERR
command &> /dev/nullcommand > /dev/null 2>&1 - Symbolic and hard links
ln -s TARGET LINK_NAMEThe best information can be found on the man page. Use man ln for further details. However, to avoid confusion, please note that the syntax is as follows: “TARGET” should be the file or directory for which you would like to create a link, while “LINK_NAME” is the name and directory where the link will appear in the specified absolute file path. It should be noted that “TARGET” should be an absolute path to the item you want to link. However, you can use relative paths for “LINK_NAME” if you wish. Nonetheless, I prefer using absolute paths for both to avoid making mistakes, such as misplacing the link on my system.
- Create symbolic link to file
$ ln -s /home/ryan/something.py /opt/scripts/something.py - Create directory with a timestamp as it’s name
timestamp=$(date +"%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S")- Then to make the directory , use the following syntax
mkdir "directory_$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S)"
- Then to make the directory , use the following syntax
- Enable vi keybinds for bash
set -o vi - Find bash shortcuts
man readline - Remove file with hyphens in the name
rm -- -filename rm ./--filename - Start comand as background job
command &
Note: Type
jobsto view your background tasks
- Resume suspended background
fg - Change file extension of all files in directory
rename 's/\.foo$/.bar/' *.foo
Note: Replace “foo” with the current extension , replace “bar” with the new ext.
- Show keycode for keybind
xev
Note: If you’re using Xorg as your display server, xev should already be installed. This tool let’s you see what keycode goes to what key.
- After finding the keycode, run this command below. Substitute \<KEYCODE\> with the numerical keycode you retrieve from xev.
```bash
xmodmap -pk | grep <KEYCODE>
```
- Show info about hard drives connected
find /dev/disk/by-id/ -type l|xargs -I{} ls -l {}|grep -v -E '[0-9]$' |sort -k11|cut -d' ' -f9,10,11,12 - Show otherboard info
dmidecode -t 2 - Disable trackpad on linux
sudo apt-get install xinput- Find the name of your touchpad
xinput listNote: Alot of the time trackpads are labeled with “SynPS/x Snynaptics TouchPad”.
- Locate the ID in the second column using the command below.
xinput --disable <ID>
- Find the name of your touchpad
- List all users on host
compgen -u | column - Restore default .bashrc, .profile
cat /etc/skel/[.bashrc,.profile,...] ~/.[bashrc,profile,etc...]
Note: The default versions of these files are usually going to be stored in /etc/skel
- Show motherboard info
dmidecode | less - Get CPU info
lscpu cat /proc/cpuinfo - Get disk info
lsblk -o +MODEL,SERIAL,WWN or ls -l /dev/disk/by-id or lsblk |awk 'NR==1{print $0" DEVICE-ID(S)"}NR>1{dev=$1;printf $0" ";system("find /dev/disk/by-id -lname \"*"dev"\" -printf \" %p\"");print "";}'|grep -v -E 'part|lvm' - Keep aliases when running scripts
shopt -s expand_aliases - Get UUID of drive
lsblk -f or sudo blkid or vim /etc/fstab -
Reduce text entering sensitivity
- Enter this line in your xinitrc , or just copy the xinitrc from the ~/dotfiles directory to your local .xinitrc
xset r rate 250 60
- Enter this line in your xinitrc , or just copy the xinitrc from the ~/dotfiles directory to your local .xinitrc
Note: You can either use kbdrate or xset , preferably xset as it works alot easier.
This will reduce the sensitivity
System Tools and 3rd party utilities command snippets
The below section should include tools and snippets from various tools i’ve used.
Minecraft
-
Download location for minecraft shader packs
Note: The xinitrc file is used for loading additional configurations and settings when the Xorg server starts.
- Manually disable the caps lock ( lock , not the button itself) using python script
python -c 'from ctypes import *; X11 = cdll.LoadLibrary("libX11.so.6"); display = X11.XOpenDisplay(None); X11.XkbLockModifiers(display, c_uint(0x0100), c_uint(2), c_uint(0)); X11.XCloseDisplay(display)'
Note: Install numlockx and run the command above
- Using setxkbmap
setxkbmap -option caps:none - Using localectl ( RHEL )
sudo localectl set-x11-keymap us "" "" caps:none - Using XKBOPTIONS ( Debian )
- Open /etc/default/keyboard
vim /etc/default/keyboard - Modify config file
XKBOPTIONS="caps:none" - Apply changes
sudo dpkg-reconfigure keyboard-configuration sudo udevadm trigger --subsystem-match=input --action=change
- Open /etc/default/keyboard
- Add aliases for ssh connections
- Open SSH config in vim
vim ~/.ssh/config - In your ssh config , add two lines for each host , one being the IP and the port you want to use
Host xxx.xxx.x.x Port xxx - Then add the IP addresses for the ssh hosts to the /etc/hosts file with the format below
IPADDR hostname
- Open SSH config in vim
-
Create swap file
- Use
ddto create the file using the /dev/zero devicedd if=/dev/zero of=/swapfile bs=1M count=100 - Convert file to swapfile
mkswap /swapfile - Swap to the newly created swap file
swapon /swapfile - Mount the file in /etc/fstab
/swapfile none swap defaults 0 0Add this line to the bottom of your /etc/fstab file. This will mount the swap file automatically after boot
- Use
Tips & tricks
Below is some useful info for different services and how they can be enabled / modified.
- Installing Network Manager on Debian 12
One of the issues while installing NetworkManager lies with a preset network configuration by the system. Specifically the file /etc/network/interfaces is configured automatically and for some reason if this is present you will see an error in STDERR when installing asking you to remove the configuration if you want to use Network manager to manage any connections.
Simply delete all lines in /etc/network/interfaces and re-install the package and the systemd service file should be present and should allow you to activate it.
ProtonVPN connections
Note: When using the pre-built OpenVPN configurations , change the file extension to a .conf file , then copy the file over to /etc/openvpn. This will start a daemon for every connection in the directory.
-
Setting up torrent server vm
-
Put ovpn file in /etc/openvpn
-
install openvpn-systemd-resolved and network manager
sudo apt install openvpn-systemd-resolved
-
Systemd
-
Change default editor for systemd edit and other sudo commands
- Set environment variables and add to your terminals config file
export EDITOR = /usr/bin/vim export SYSTEMD_EDITOR = /usr/bin/vim export VISUAL = /usr/bin/vim - Then add the following lines in your visudo configuration
Run
sudo visudoand add the following lines``` Defaults env_keep += "EDITOR VISUAL SYSTEMD_EDITOR" Defaults editor = /usr/bin/vim ```Then re-log into root user and test
- Set environment variables and add to your terminals config file
- Stop the service
systemctl stop <unit-name> - Disable unit
systemctl disable <unit-name> - Stop the unit from being started manually or automatically
systemctl mask <unit-name> - Systemd timer unit template
[Unit] Description=Runs My Service every hour [Timer] OnBootSec=10min OnUnitActiveSec=1h Unit=my-service.service [Install] WantedBy=timers.target - List all Systemd timers
systemctl list-timers --all - Check when Systemd timer will go off
systemctl status timer-name.timerNote: After running this command , you should see a “Trigger” section in the output. This field tells you when the timer will go off next.
- Configure unit to run command when stopping / exiting
ExecStop=/path/to/command
Note: Put this snippet under the “Service” section
- Creating service files that involve X org server
PartOf=graphical-session.target
If you need to create a service that depends upon an X server running , add this line under the “Unit” section. Also you will want to add this line under the “Install” section.
- Config for unit which requires X server to be running
WantedBy=xsession.target - Boot into different target
- Search for all targets you can boot into
cd /usr/lib/systemd/system grep Isolate *.target - Decide which target you would like to use , then run systemctl isolate
systemctl isolate something.target
- Search for all targets you can boot into
- Start systemd service under specific User ID
systemctl --user service.name - Change user systemd service to start on system startup
loginctl enable-linger myuser
Running scripts at startup
- Using Rc.local
sh /home/user/scriptdir/script.sh
Add the line above in the /etc/rc.d/rc.local file
- Using Systemd unit file
[Unit] Description=Reboot message systemd service. [Service] Type=simple ExecStart=/bin/bash /home/ec2-user/reboot_message.sh [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.targetUse the template above for your script , put this inside /etc/systemd/system
- Set perms for the service file
chmod 644 /etc/systemd/system/script.service - Enable the service file in systemd
systemctl enable script.service - Using Crontab
- Edit the crontab file
crontab -e - Configure crontab to run script on reboot
@reboot sh /home/user/reboot_message.sh
Note: To run the script on reboot, paste the following snippet and replace the “/home/user/reboot_message.sh” with the path of your scripts. Please note that not all versions of cron support the ‘@reboot’ option
- Using init.d
-
Make a script and put it in /etc/init.d/ Use the template below :
!/bin/sh case "$1" in start) # Executes our script sudo sh /home/user/script.sh ;; *) ;; esac exit 0
Xrandr
- Configuration
Note: Put xrandr configurations in ~/.xprofile
- Move monitor to the right of another
xrandr --output <DISPLAY-OUTPUT-1> --right-of <DISPLAY-TWO-2>
Note : if you’re unsure which display output to use, run the
xrandrcommand once to see all available displays to choose
- Change refresh rate of monitor
xrandr --output <DISPLAY-OUTPUT> --mode <DISPLAY-RESOLUTION> --rate <REF-RATE>
Note: Put this line in the ~/.xprofile file for configuration on startup ( happens late in the boot process )
-
Change background picture with feh
- Set wallpaper with Feh
feh --bg-fill /home/user/something.jpg - Then put this line in your ~/.xinitrc file
~/.fehbg &
- Set wallpaper with Feh
Note: create a ~/.fehbg file with your feh command
nmcli & Networking
- Check for openports
netstat -tulnp ss -tulnp -
Change subnet mask of existing connection using nmcli
- Bring up interface manually using ip tool
sudo ip link <interface> up - Show service being used by specific port
lsof -i tcp:80 lsof -i :80
Note: This example prints out processes using the “80” port which is commonly used for HTTP
- Remove Secondary IP for host
nmcli con mod <con-name> -ipv4.addresses "<IP>" - Add Wifi Connection
nmcli device wifi connect <AP name> password <password> - Create new network connection in nmcli
nmcli con add con-name static ifname ens18 autoconnect no type ethernet ip4 10.0.0.10/24 gw4 10.0.0.1 ipv4.method manual - Bring up network connection with nmcli
nmcli con up <con-name> - Switch to DHCP with nmcli
nmcli con up dhcp - Change connection to not connect automatically with nmcli
nmcli con mod <con-name> connection.autoconnect no - Add DNS server to connection with nmcli
nmcli con mod <con-name> ipv4.dns <dns-server-ip> - To add additional dns servers
nmcli con mod <con-name> +ipv4.dns 8.8.8.8 - Change IP for existing connection in nmcli
nmcli con mod <con-name> ipv4.addresses <ip-address>/<CIDR-prefix> - Add secondary IP addresses with nmcli
nmcli con mod <con-name> +ipv4.addresses <new-ip>/<CIDR-prefix> - After chaning any properties to a connection you must re-activate the connection
nmcli con up <con-name> - Add custom IPv4 route to connection
nmcli conn modify "Connection name" +ipv4.routes "<network-addr>/<prefix> <gateway-ip> [metric]" # Example nmcli con mod "eth0" +ipv4.routes "192.168.3.0/24 192.168.3.1"- The
metricis an optional command which determines the priority of the route
- The
- Create static connection manually ( Example )
nmcli con modify "eth0" \ ipv4.addresses "192.168.3.100/24" \ ipv4.gateway "192.168.3.1" \ ipv4.dns "1.1.1.1" \ ipv4.method manual
- Disable IPv6
sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=1
Packet Capturing
Tshark
- Capture traffic on specified interface
tshark -i <interface> - Capture & Save traffic on specified interface to a file
tshark -i <interface> -w capture.pcap - View capture from file
tshark -r capture.pcap - Search for specific port in capture
tshark -r path_to_file.pcap -Y "tcp.port == 6881 || tcp.port == 6889 || tcp.port == 51413"
TCPDUMP
- Search for specific port in capture
sudo tcpdump -r path_to_file.pcap 'tcp port 6881 or tcp port 6889 or tcp port 51413'To specify a port range
sudo tcpdump -r path_to_file.pcap 'tcp portrange 6881-6991' - Check if Wake-on-LAN port is open
tcpdump -i <interface-name> udp port 9 - Scan interface for SYN port scans
tcpdump -i <interface> 'tcp[tcpflags] & (tcp-syn) != 0' - Sniff for SYN packets
sudo tcpdump -i <interface> 'tcp[tcpflags] & (tcp-syn) != 0'
SELinux
- Put SElinux into disabled mode in grub
selinux=0
Note: Put this line into your kernel boot args
- Put Selinux into enforcing mode in grub
enforcing=0
Note: Add this to kernel boot args
- View selinux config
cat /etc/sysconfig/selinux - Check what mode selinux is running
getenforce -
Switch between selinux modes temporarily
- permissive mode
setenforce 0 - enforcingm mode
setenforce 1
- permissive mode
- Switch modes persistantly
Note: Modify /etc/sysconfig or add kernel boot arg
- Get status of selinux
```bash
sestatus
```
- Get selinux status
setstatus -v -
Show context setttings
- using ls
ls -Z - using ps
ps Zaux - using ss
ss -Ztul
- using ls
-
Setting Context types
- Add context type to manually created directories
semanage fcontext -a -t <contxt-type> "/mydir" - Apply policy settings
restorecon -R -v /mydir
- Add context type to manually created directories
- Help with setting contexts
man semanage-fcontext - Finding context types
dnf -y install selinux-policy-package man -k _selinux
Note: Install selinux-policy-doc package
- Enable ssh port in SELinux
semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp PORTNUMBER - Relabel entire filesytem
restorecon -Rv /- Create .autorelabel after modifications
/.autorelabel
- Create .autorelabel after modifications
Note: This works after server restart, afterwards the file will be removed
-
Managing Port Access
- Example: Changing port of apache
semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 8008 - Template
semanage port -a -t <context-type> -p <tcp/udp> <port>
- Example: Changing port of apache
Note: Run
restoreconwhen finished to apply changes.
-
Using Boolean Settings to Modify SELinux Settings
- Get list of booleans on system
getsebool -a semanage boolean -l - Change Boolean example
setsebool ftpd_anon_write on - Template
setsebool <context-rule> <on/off>
- Get list of booleans on system
- Apply permanant changes to boolean
setsebool -P -
Diagnosing and Addressing SELinux Policy Violations
- audit log
Note: The audit log is stored in /var/log/audit/audit.log.Messages are logged with the type=AVC in the log.You can search for these messages through grep
- Search audit messages in Grep
grep AVC /var/log/audit/audit.log
Note: “avc: denied { map } “ indicates a map request was denied , therefore some process tried to read attributes of a file and that was denied. Thus triggering a policy violation. In this logging , the scontext is the source context while the tcontext is the target context
-
Making SELinux Analyzing Easier
- Download the sealert command
dnf -y install setroubleshoot-server
- Download the sealert command
Note: Once finished downloading ,restart your server.Then you can grep for entries from sealert.
- Grep for sealert entries
journalctl | grep sealert
Note: From the info you get , you might see a command it recommends to run to see further info.
- Check sealert logging
sealert -l <SOME-ID>
Note: Sometimes the logging will even recommend other commands to run in order to fix the issue, take these commands with a grain of salt unless you know what you are doing .These recommendations will have a confidence score
-
Key topics about selinux
-
newly created files inherit the context settings from the parent directory
-
copied files do this as well.
-
DNF
- Search for RPM’s of specific tool
dnf whatprovides */semanage dnf whatprovides - Undo recent download
dnf history undo <ID>
Adguard Home
-
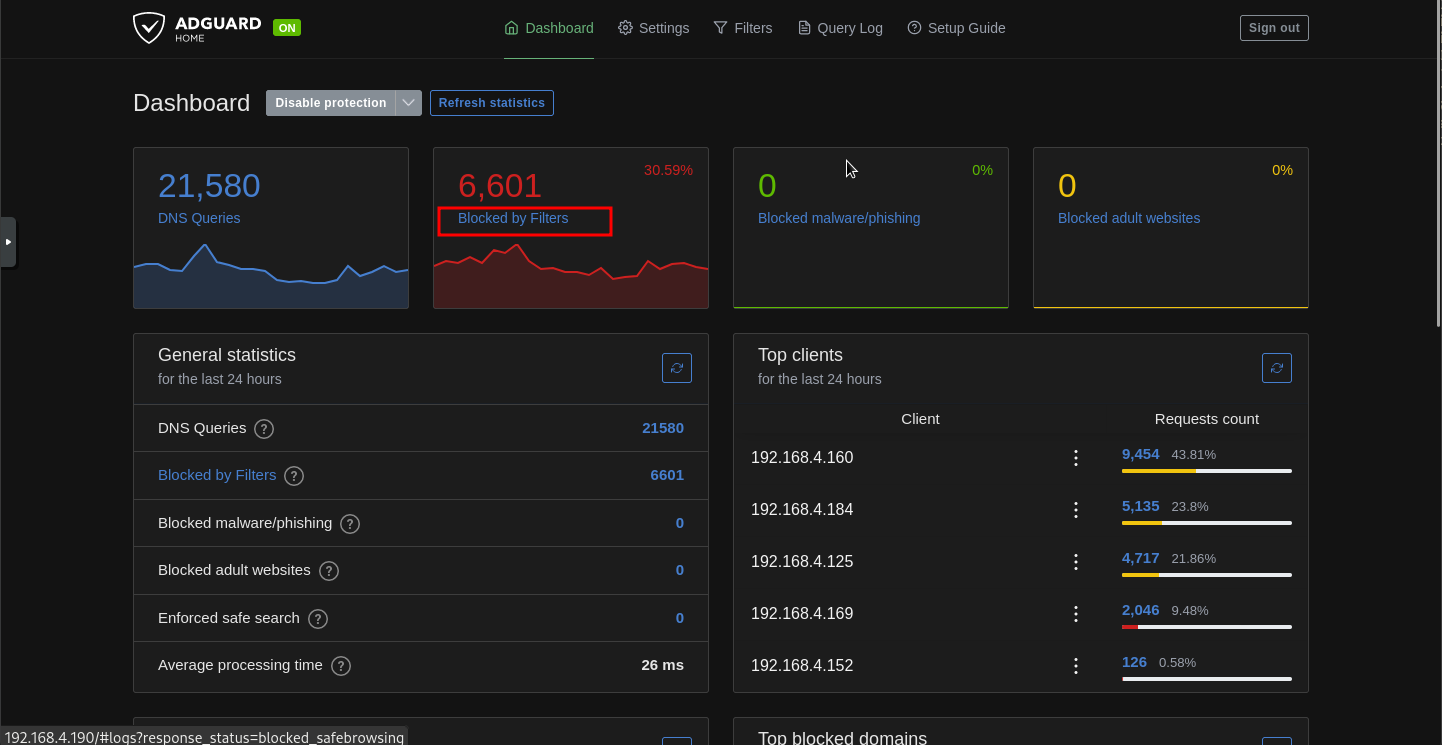
Error: “X” Service is blocked !
- Log onto your adguard home page and click on the Blocked by Filters button
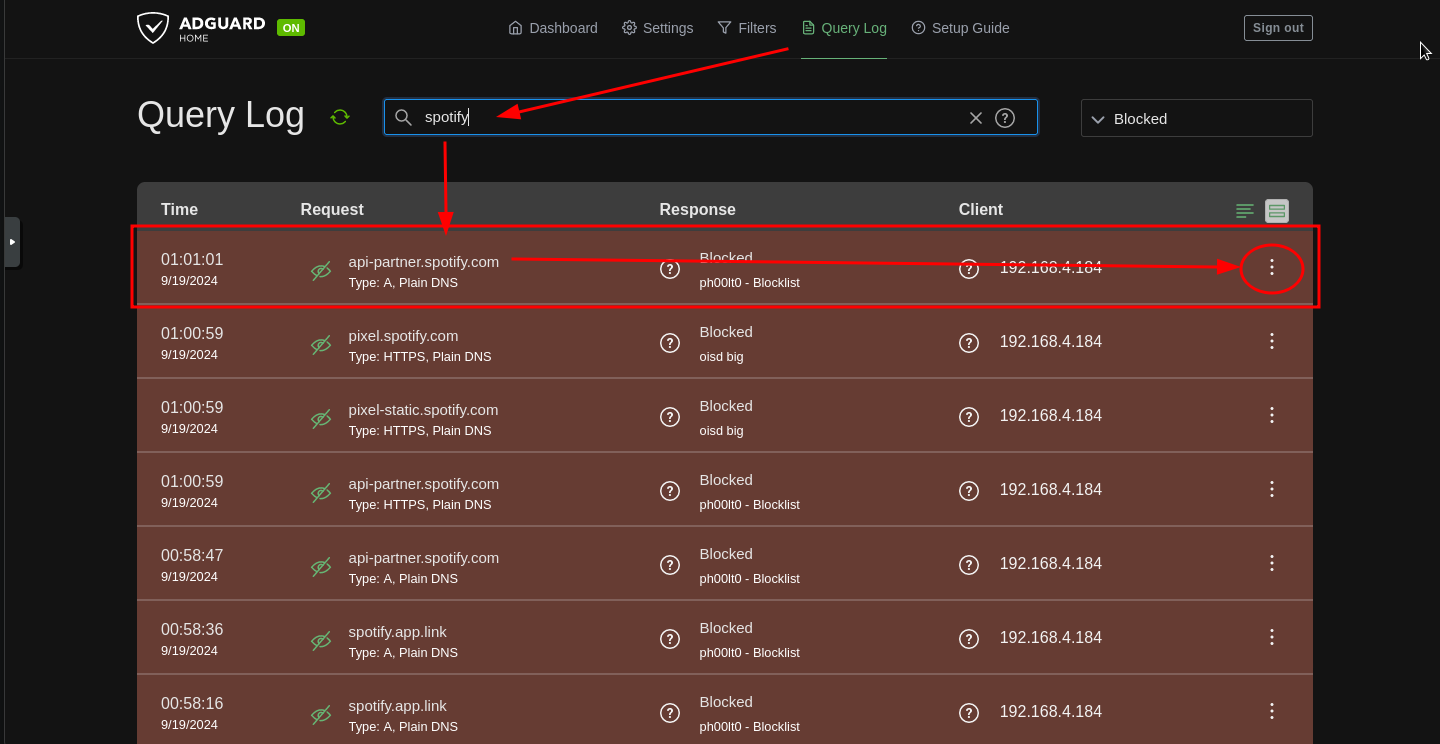
2. Then search for the domain you would like to block
3. Select the side menu on the right hand side and click "Unblock"
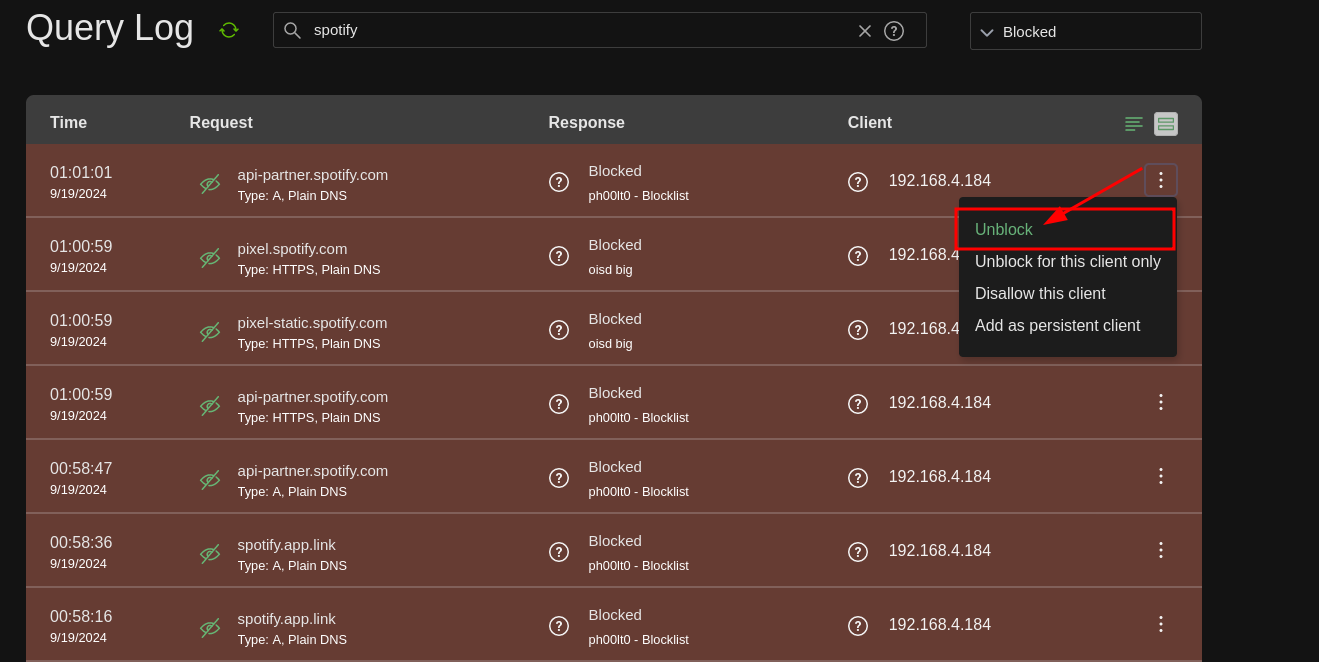
And after that you’re done !
NFS
- Setup NFS on RHEL 9
- Create nfs directory to be shared
mkdir -p /nfsdata /users/user1 /users/user2 - Create /etc/exports file and assign the following
/nfsdata *(rw,no_root_squash) /users *(rw,no_root_squash) - Install the cifs-utils package
dnf install -y nfs-utils - Add the nfs , rcp-bind, and mountd services to firewall
firewall-cmd --add-service nfs --permanent ; firewall-cmd --add-service rpc-bind ; firewall-cmd --add-service mountd --permanent - Then reload the firewall-cmd config
firewall-cmd --reload
- Create nfs directory to be shared
- List available mounts from IP or hostname
showmount -e <IP-or-hostname> - Perform pseudo root mount
mount <Ip-Or-hostname>:/ /mnt
NTP
- Turn on NTP
timedatectl set-ntp 1 - Convert epoch time to human time
date --date '@1720893005 - Show the current system day of month, month , and year
date +%d-%m-%y - Set the current time 3 minutes past 4 pm
date -s 16:03 - Synchronize curent system time to the hardware clock
hwclock --systohc - Synchronize current hardware time to the system clock
hwclock --hctosys - Show current time settings
status - Set current time
set-time TIME - Set timezone
set-timezone ZONE - Show a list of all time zones
list-timezone - Control whether to use RTC ( hardware clock )
set-local-rtc [0|1] - Control whether NTP is enabled
set-ntp [0|1]
Note: timedatectl is used to switch on NTP time , it talks to the chronyd process
Podman
- Run container in detached mode
podman run -d nginx - Run container in TTY mode
podman run -it nginx /bin/sh - View running containers
podman ps - View all inactive and active containers
podman ps -a - Attach to running container
podman attach <name> - Stop running container
podman stop <name> - Search which registries are currently used
podman info - Filter images in search
podman search --filter official=true alpine or podman search --filter stars=5 alpine - Pull image
podman pull <image> - Build custom image
podman build -t imagename:tag -f /path/to/Containerfile- Example
podman build -t mymap:1.0
- Example
- Verify custom image was built
podman images - Remove images with None tag
podman image prune - Send SIGTERM signal to the container ,
bash podman stop
Note : If no results after 10 seconds , the SIGKILL signal is sent.
- Kill container
podman kill
Note: Immediately sends the SIGKILL command
- Restart container
podman restart - Remove container
podman rm
Note: Removes container files written to the writable layer
- Run container and delete container files automatically
podman run --rm - Running Commands inside containers
podman exec mycontainer uname -r- TTY MODE
podman exec -it mycontainer /bin/bash
- TTY MODE
- Managing Container Ports
podman run --name nginxport -d -p 8080:80 nginx
Note: Ports 1-1024 are accessible by the root user only. To run a container with port forwarding , run the following command below. This would allow the nginx process to access host port 8080 and forward to standard http port 80 .After adding the port , don’t forget to add the port to your firewall
- Managing Container Environment Variables
For containers such as mariadb , you will need to supply the container with environment variables. For example the mariadb container needs the password for the root user.
Some containers contain a “usage” line that may say how the container needs to run with environment variables included. However this is not always the case, you can check the container with podman inspect to see if it’s there.
- Mariadb container example
```bash
podman run -d -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=password -e MYSQL_USER=anna
```
- Managing Container storage
Note: If you want to save the changes made in the writable layer , you will need to configure persistant storage. You can do this by adding a bind-mount from the host OS into the container, this is used instead of a block device
There are 2 requirements to doing this however :
- The host directory must be writable for the user account that runs the container
- The appropriate SELinux context label must be set to container_file_t
Note: The bind-mount dir must be OWNED by the user that runs the container.
- Configure bind mount to be owned by running user
```bash
semanage fcontext -a -t container_file_t "hostdir(/.*)?"; restorecon
```
- To do so automatically
```bash
-v host_dir:container_dir
```
- If root container or if user is owner of the container
```bash
-v host_dir:container_dir:Z
```
-
Set directory ownership on bind-mounted directories for rootless containers
- Find UID of the user that runs the container main app
podman inspect imagename - set the container UID as the owner of the directory on the host
podman unshare chown nn:nn dirname
- Find UID of the user that runs the container main app
Note: To set the container UID as the owner of the directory on the host. This directory must be in the rootless user home dir. Otherwise it woulden’t be apart of the user namespace.
3. Verify the user ID mapping
```bash
podman unshare /cat/proc/self/uid_map
```
4. Verify that the mapped user is owner on the host
```bash
ls -ld ~/dirname
```
-
Running Containers as Systemd Services
- Generate Systemd unit for container
podman generate systemd --name mycontainer --files - Create this dir and CD to it, then run
podman generate - Enable container as Systemd service
systemctl --user enable containe-mycontainer.service
- Generate Systemd unit for container
Note: The Container file must be generated in the
~/.config/systemd/user/directory
Package management with DNF
- Add installation disk as repo
- Add repo file using config-maanger
dnf config-manager --add-repo=file:///repo/filename -
Then locate the repo in /etc/yum.conf.d
- add the ‘gpgcheck=0’ to the file
- Add repo file using config-maanger
Logical Volume Managment
- View volume groups extent size
vgdisplay - Create VG with specified extent size
vgcreate myvg /dev/sdx -s 8MiB
Note: The example above creates a volume group with a Physical Extent size of 8-MiB
- Create logical volume with specific size
lvcreate -n lvdata -l 50%FREE vgdata or lvcreate -n lvdata
CIFS
-
Enable CIFS mounts for user
- Set the SUID perm on these binaries [ /bin/mount, /bin/umount ,/user/sbin/mount.cifs ]
sudo chmod u+s /bin/mount /bin/umount /usr/sbin/mount.cifs
- Set the SUID perm on these binaries [ /bin/mount, /bin/umount ,/user/sbin/mount.cifs ]
-
CIFS default ports
CIFS uses ports 138 for clients , 139 & 445 for servers
GRUB
- Re-add windows to grub 2 boot menu
- Enable os-prober
- Open grub config on local host
sudo vim /etc/default/grub - Add the following line to the end of the file
GRUB_DISABLE_OS_PROBER=false - Once you are done , update grub config ( Ubuntu )
sudo update-grub
- Open grub config on local host
- Error : “Unable to mount root fs on unknown block”
-
Check grub config for image Check the configuration of the target in the grub menu , if the root filesystem is pointed to a “/dev/sda” drive, this is likely the issue. In general you want to use UUID’s as they are hard coded identifiers for each specific drive.
-
Update GRUB config
Find the UUID of the drive where your root filesystem is mounted, add this UUID into your grub config under “GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT” or “GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX”. Replace the value within with the UUID of the drive.
Note : os-prober is disabled by default on ubuntu for security, this is most likely why your grub is not showing your windows installation if you’re dual booting.
-
Reset root password without access to wheel group
-
Boot into GRUB boot args
-
Remove the “rhgb” and “quiet” from the options
-
add “init=/bin/bash”
- then mount the filesystem as writable
mount -o remount,rw / - Then change the password for root with
passwd root - Then enable SELinux relabeling on next boot
touch /.autorelabel - then reboot the system
/usr/sbin/reboot -f
-
User management
- View user ID
id -u <username> - Change password validity to 90 days
passwd -n 30 -w 3 -x 90 username - Change password validity to 90 days using chage
chage -E 2025-12-31 username
Note: The “-n” sets minimal usage period “-w” sets the days the user will be warned before their password expires “-x” sets the amount of days until the password expires You can also do this with chage by setting an exact date
- find the amount of days until the password expires
chage -l usernameNote: You can also do the same by viewing the /etc/passwd file
-
Change default password expiration
-
open the /etc/login.defs file
-
change PASS_MAX_DAYS to the number of days before the password expires
-
- Add default directories for newly created users
- Cd to /etc/skel directory
cd /etc/skel - Modify the .bashrc file in /etc/skel
- Cd to /etc/skel directory
Note: This bashrc will now be used for all created users
-
Change default UUID for new users
-
Open /etc/login.defs
-
Locate and modify the two lines below
UID_MIN 1000 UID_MAX 60000
-
- View what groups a user is apart of
lid username - Change home directory of user with usermod
usermod -d /home/NEW-DIR/ *username* or usermod -m -d /home/NEW-DIR/ *username*
Note: You can use the
-moption to move the contents of the users current home directory to the newly created home directory.
- Add user to group
usermod -aG <group-name> <username> - Change UID of user
usermod -u <NEWUID> username - Configure user to be unable to start interactive shell
usermod -s /sbin/nologin username - Change group owner of dir
chown -R :groupname /dirname - Change permissions for group on dir
chmod g+rwx /dirname
Note: This example allows full access to the dir for the group members
-
Configure dir where new files are owned by group
- Set the SGID on the directory
chmod g+s /dirNote: This change configures
/dirto assign all newly created files to the group of the user
- Set the SGID on the directory
- Change username of user
usermod -l [new_user] [old_user] or sudo usermod -l faruk -d /home/faruk -m pardus - Update GRUB config
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/efi/EFI/almalinux/grub.cfg grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/efi/EFI/redhat/grub.cfg - Reset root password
-
Add init=/bin/sh in GRUB kernel boot args
- Remount filesystem for writing
mount -rw -o remount / - Use passwd to change pass
passwd root - Create autolabel file
touch /.autorelabel
Common errors and small fixes
-
Error: org.bluz.Error.NotReady
- Using the rfkill tool
sudo rfkill unblock all
- Using the rfkill tool
Docker
- Connect docker container to network
docker network connect <network-name> <container-name-or-id> -
View docker network configuration
docker network inspect <container-id-or-name> - Create docker network
docker network create <network-name> - Re-Attach to docker container
docker attach <container-id-or-name> - Attach with bash TTY
docker exec -it <container-id-or-name> /bin/bashto detach , press CTRL + P followed by CTRL + Q
- Change configuration of apache web container
- list docker networks
sudo docker network ls
- delete all docker containers
docker rm vf $(docker ps -a -q)
- Add bind mount to docker container
docker run -v /var/something/something:/var/container/something somethingYou can use the “-v” option when making bind mounts the left operand is the file path of a directory on your local machine , the other operand is where that path will be mounted to in the containers file system
- Stop Docker compose run ( in parent directory )
docker compose down - Stop specified docker compose run
docker compose -f /path/to/compose.yml down -
Connect container to protonvpn container using Docker Compose In your compose.yml file , add the following
- Start bash TTY in container
docker exec -it <container-id> /bin/bash
Oracle SBC
- Show all sip agents
sho sipd agents - Show configuration for specified agent
sho configuration session-agent <AGENT-NAME> sh
TrueNAS
- Restart ssh service
midclt call service.restart "ssh"
Unzip
unzip all zip files in directory
unzip \*.zip
Display Management
check what display manager you are using
On Debian/Ubuntu using X11 :
cat /etc/X11/default-display-manager
or
dpkg -l | grep -E 'gnome|kde|xfce|lxde|mate'
On Redhat :
cat /etc/sysconfig/desktop
rpm -qa | grep -E 'gnome|kde|xfce|lxde|mate'
Check current display session:
echo $DESKTOP_SESSION
Check process list for running DE :
ps -e | grep -E 'gnome|kde|xfce|lxde|mate'
check what compositor you are using
sudo apt install -y inxi
inxi -Gxx | grep compositor
Xorg
Make desktop shortcut for application
If you’re on GNOME , you can make a shortcut using the gnome-desktop-item-edit tool
gnome-desktop-item-edit ~/.local/share/applicationsj --create-new
You will need to do this if you would like the application to show up in the GNOME search menu.
Create a file for the shortcut located in /usr/share/applications. Create file with *.desktop extension
Use the template below to create your shortcut
Or you can do it manually by using this template for the *.desktop file
[Deskktop Entry]
Encoding=UTF-8
Version=1.0 # version of an app.
Name[en_US]=yEd # name of an app.
GenericName=GUI Port Scanner # longer name of an app.
Exec=java -jar /opt/yed-3.11.1/yed.jar # command used to launch an app.
Terminal=false # whether an app requires to be run in a terminal.
Icon[en_US]=/opt/yed-3.11.1/icons/yicon32.png # location of icon file.
Type=Application # type.
Categories=Application;Network;Security; # categories in which this app should be listed.
Comment[en_US]=yEd Graph Editor # comment which appears as a tooltip.
disable sleep / suspend on xorg
Create the /etc/systemd/sleep.conf.d/nosuspend.conf file
Add these lines to the file
[Sleep]
AllowSuspend=no
AllowHibernation=no
AllowSuspendThenHibernate=no
AllowHybridSleep=no
create
/etc/X11/xorg.conf.d/10-extensions.conf
Then put this into the conf file
Section "Extensions"
Option "DPMS" "false"
EndSection
Rclone
copy files from source to dest
rlcone copy /source/dir mydrive:/drive/dir
Du
show all files in current directory size in different units The 3 lines below shows the sizes in kilobytes
du -k *du --block-size=1K *du -B 1K *Note
- You can substitute the ‘k’ for other letters which represent other file size units : M,K,G,T,E,Z,Y
- List largest files in current directory
du . | sort -nr | head -n10
- List largest directories in current directory
du -s * | sort -nr | head -n10
- List disk size of all dotfiles
du -sh .??* - Exclude files below a certain size threshhold
du -t 1K - Exclude files above a certain size threshhold
du -t -1K
Note : Read the Du manual under the SIZE section for valid formats for the threshhold size
Markdown
Markdown table template
| Left Align (default) | Center Align | Right Align |
| :------------------- | :----------: | ----------: |
| React.js | Node.js | MySQL |
| Next.js | Express | MongoDB |
| Vue.js | Nest.js | Redis |
Output :
| Left Align (default) | Center Align | Right Align |
|---|---|---|
| React.js | Node.js | MySQL |
| Next.js | Express | MongoDB |
| Vue.js | Nest.js | Redis |
Youtube downloading
download only the transcript
yt-dlp --verbose --skip-download --write-subs --write-auto-subs --sub-lang en --sub-format ttml --convert-subs srt --output "transcript.%(ext)s" <PUT-URL-HERE> && sed -i '' -e '/^[0-9][0-9]:[0-9][0-9]:[0-9][0-9].[0-9][0-9][0-9] --> [0-9][0-9]:[0-9][0-9]:[0-9][0-9].[0-9][0-9][0-9]$/d' -e '/^[[:digit:]]\{1,3\}$/d' -e 's/<[^>]*>//g' ./transcript.en.srt && sed -e 's/<[^>]*>//g' -e '/^[[:space:]]*$/d' transcript.en.srt > output.txt && rm transcript.en.srt
Serial Communication
- No /dev/ttyUSBx showing for connected serial cable
- Check if proper drivers are loaded
lsmod | grep -E 'ch341|ftdi_sio' - If output from previous command is blank , load drivers using modprobe
sudo modprobe ch341 sudo modprobe ftdi_sio - Install usbutils package
sudo apt install usbutils - run dmesg and re-plug cable
dmesg | tail -n 20
- Check if proper drivers are loaded
Jekyll
- Generate Jekyll template project
jekyll new <name-of-project> - Host Jekyll site locally
- cd to project directory and install Dependencies
bundle install - Start Jekyll server and host locally
bundle exec jekyll serve
- cd to project directory and install Dependencies
Note : Site should be available at
http://localhost:4000
ChatGPT CLI
- Installation script
curl -L -o chatgpt https://github.com/kardolus/chatgpt-cli/releases/latest/download/chatgpt-linux-amd64 && chmod +x chatgpt && sudo mv chatgpt /usr/local/bin/
Rust
- Install Rust
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh
Zsh
Install ZSH
- Using curl
sh -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ohmyzsh/ohmyzsh/master/tools/install.sh)" - Using wget
sh -c "$(wget -O- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ohmyzsh/ohmyzsh/master/tools/install.sh)" - Using fetch
sh -c "$(fetch -o - https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ohmyzsh/ohmyzsh/master/tools/install.sh)"
Verify which source file zsh is going to use
print -r -- ${ZDOTDIR:-$HOME}
Note: All of this was taken from the README.md for Zsh on their Github. I’ll paste a link below for easy reference
Curl
curl -L https://somedir.com -> used to follow links using https, “-L” option tells curl to follow redirects
Snapper
Used to create snapshots of BTRFS subvolumes
Bspwm
bspc wm -r: restart bspwm
Tmux
tmux attach-session -t <int or string> -> Re-attach to tmux session , detach with Prefix-D
Tmux work environment startup script
This script below sets up 3 windows , the first opens up 3 files in separate tabs in vim , the second and the third opens a directory in ranger.
#!/bin/bash
# Name for tmux session
session="Work"
# Create new session
tmux new-session -d -s $session
# New window, open tickets.md notes.md scratch.md in individual tabs in vim
# Command: vim $HOME/notes/tickets.md -p $HOME/notes/notes.md -p $HOME/notes/scratch.md
tmux rename-window -t 0 'work'
tmux send-keys -t 'work' 'vim $HOME/notes/tickets.md -p $HOME/notes/notes.md -p $HOME/notes/scratch.md' C-m
# New window named 'todo' , open todo directory in ranger
# Command: ranger $HOME/todo
tmux new-window -t $session:1 -n 'todo'
tmux send-keys -t 'todo' 'ranger $HOME/todo' C-m
# New window named 'notes' , open wiki document directory in ranger
# Command: ranger $HOME/wiki/_docs
tmux new-window -t $session:2 -n 'notes'
tmux send-keys -t 'notes' 'ranger $HOME/wiki/_docs' C-m
# Attach to the newly created session
tmux attach-session -t $session:0
Ranger
Generate config for ranger
ranger --copy-config=all
Bashrc function to CD to dir when exiting ( Bash / zsh )
ranger() {
tempfile="$(mktemp -t ranger-cd.XXXXXX)"
command ranger --choosedir="$tempfile" "$@"
if [ -f "$tempfile" ] && [ "$(cat "$tempfile")" != "$(pwd)" ]; then
cd -- "$(cat "$tempfile")"
fi
rm -f "$tempfile"
}
Same as above but for fish shell
function ranger
set tempfile (mktemp -t ranger-cd.XXXXXX)
command ranger --choosedir=$tempfile $argv
if test -f $tempfile
set dir (cat $tempfile)
if test -d "$dir" -a "$dir" != (pwd)
cd $dir
end
rm -f $tempfile
end
end
Ensure ranger will output the last dir to the file specified by --choosedir
set choose_dir=True
Diff
Basic Usage
diff old_file new_file
- Compares line-by-line.
- Symbols:
<= line only inold_file>= line only innew_file
Unified Format (Recommended for Readability)
diff -u old_file new_file
- “Unified diff” format with context.
- Symbols:
-= line removed+= line added- context lines are unchanged lines
Example:
@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
+New line added
Line 1
-Line 2
+Line 2 modified
Line 3
Side-by-Side Comparison
diff -y old_file new_file
- Shows files side-by-side.
- Indicators:
|= difference<= only inold_file>= only innew_file
To hide matching lines:
diff -y --suppress-common-lines old_file new_file
Ignore Whitespace Changes
If formatting differences don’t matter:
diff -u -w old_file new_file
Or side-by-side ignoring whitespace:
diff -y -w old_file new_file
Test with Sample Files
echo -e "one\ntwo\nthree" > file1.txt
echo -e "one\n2\nthree" > file2.txt
diff -u file1.txt file2.txt
Summary of Flags
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
-u | Unified diff (recommended) |
-y | Side-by-side comparison |
-w | Ignore all whitespace |
--suppress-common-lines | Hide lines that are the same |
Unsorted helpful one liners
Ping all hosts in /etc/hosts file
for x in $(cat /etc/hosts | grep -v '#' | awk -F " " '{print $1}'); do ping -c 4 $x; done